What is a Thin Film Ceramic PCB?
Thin Film Ceramic PCBs Manufacturer.Our company specializes in manufacturing high-quality thin film ceramic PCBs, known for their superior thermal conductivity, electrical performance, and mechanical stability. We utilize advanced fabrication techniques to produce reliable and precise circuit boards suitable for demanding applications in electronics, telecommunications, and automotive industries. With a commitment to excellence, we ensure our products meet the highest standards of quality and reliability.
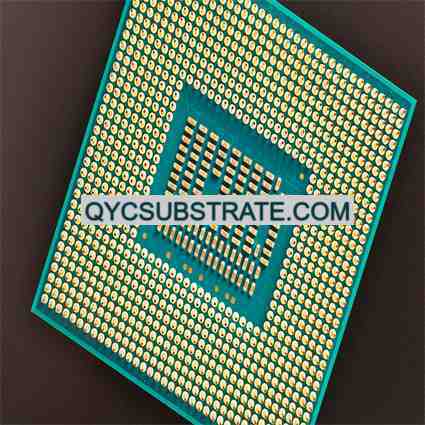
Thin Film Ceramic PCBs are advanced circuit boards featuring a thin ceramic substrate with conductive films deposited to create the circuit patterns. Unlike traditional PCBs that use thicker substrates, thin film ceramic PCBs use a very thin ceramic layer, which allows for high precision and miniaturization in electronic designs. These PCBs are particularly well-suited for applications demanding high performance, such as in high-frequency and high-power electronics.
The ceramic used in thin film PCBs is often composed of materials like alumina (Al₂O₃) or other advanced ceramics, and the thin film circuits are created by depositing conductive layers onto the ceramic base. The result is a compact, high-performance circuit board ideal for applications where space and precision are critical.
The Types of Thin Film Ceramic PCBs
Thin Film Ceramic PCBs are available in various configurations to meet different needs.
Single-layer thin film ceramic PCBs have a single layer of ceramic with conductive films applied to form the circuit patterns. These PCBs are suitable for simpler circuit designs where high precision and compact size are necessary.
Multi-layer thin film ceramic PCBs consist of several layers of thin film ceramics, each with its own conductive patterns. This design allows for more complex circuits and additional functionality while maintaining a thin profile, making it ideal for high-density electronic systems.
Thin Film Ceramic PCBs Manufacturer
Hybrid thin film ceramic PCBs combine thin film ceramics with other materials, such as organic substrates or metals. This hybrid approach allows for the customization of performance characteristics to meet specific application needs.
Custom thin film ceramic PCBs are designed to address unique requirements, including specialized circuit patterns, integrated components, or particular thermal management features. These custom designs are used in advanced applications where standard solutions do not suffice.
The Advantages of Thin Film Ceramic PCBs
Thin Film Ceramic PCBs offer several key advantages over traditional PCB materials. They are known for their high precision and accuracy, which is crucial for applications requiring exact circuit patterns and component placements. The thin ceramic substrate provides improved electrical performance, including low signal loss and high-frequency stability, essential for high-speed and high-frequency applications.
The compact and lightweight nature of thin film ceramic PCBs is another significant benefit, making them suitable for designs where space and weight are limited. Additionally, these PCBs provide effective thermal management due to the ceramic’s high thermal conductivity, helping to dissipate heat efficiently in high-power applications.
The reliability and durability of thin film ceramic PCBs are also noteworthy. They are less prone to mechanical stress and environmental degradation compared to traditional PCBs, ensuring long-term performance and stability. Moreover, the ability to support miniaturized designs is important for various industries, including consumer electronics and medical devices.
How to Design a Thin Film Ceramic PCB
Designing a Thin Film Ceramic PCB involves several important steps. The process begins with defining the requirements of the application, including electrical specifications, thermal management needs, and mechanical constraints. Selecting the appropriate ceramic material and conductive films is crucial to meet these specifications.
Creating a detailed circuit schematic is the next step, which outlines the components and their connections. This schematic serves as the foundation for the PCB layout. Using PCB design software, a layout is developed that includes the placement of components and the routing of conductive traces. The layout should be optimized for the thin film process to minimize signal losses and interference.
Patterning the conductive films involves creating precise circuit patterns using techniques such as photolithography. After patterning, any excess material is removed through etching processes. Surface finishing may include additional metal plating or protective coatings to enhance solderability and protect the conductive traces.
Finally, the design files are prepared for fabrication, and the PCB is manufactured. This process includes thin film deposition, patterning, and assembly. Testing and inspection follow to ensure that the final PCB meets all required specifications, including electrical performance and dimensional accuracy.
Why Use Thin Film Ceramic PCBs Over Other Boards?
Thin Film Ceramic PCBs provide several advantages compared to other PCB materials, particularly in high-performance and miniaturized applications. The high precision and accuracy offered by thin film technology are crucial for maintaining signal integrity in high-frequency circuits.
The improved electrical performance, including low signal loss and high-frequency stability, makes thin film ceramic PCBs ideal for applications requiring high-speed data transmission. Their compact and lightweight design is advantageous in applications with space and weight constraints.
Effective thermal management is another benefit, as the ceramic substrate helps dissipate heat efficiently, which is important for high-power applications. The high reliability and durability of thin film ceramic PCBs, coupled with their ability to support miniaturized designs, make them suitable for various advanced electronic systems.
What is the Thin Film Ceramic PCB Fabrication Process?
The fabrication process of Thin Film Ceramic PCBs involves several specialized steps. It begins with preparing the ceramic substrate, which is typically a thin profile of advanced ceramics. Thin film layers are then deposited onto the ceramic substrate using techniques such as sputtering, evaporation, or chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
After deposition, the thin film layers are patterned to create the circuit traces, pads, and vias. This is done using precision patterning techniques like photolithography. The excess thin film material is then removed through etching.
Surface finishing processes, such as metal plating or protective coatings, may be applied to improve the PCB’s performance and appearance. The final steps involve assembling components onto the PCB and conducting rigorous testing and inspection to ensure the PCB meets all required specifications.
The Application of Thin Film Ceramic PCBs
Thin Film Ceramic PCBs are utilized in a variety of advanced applications. They are commonly used in RF and microwave systems, such as communication equipment, radar, and satellite technology, where high-frequency stability and precision are crucial.
In aerospace and defense, these PCBs are employed in avionics, navigation systems, and military electronics, benefiting from their compact size and high reliability. Medical devices also make use of thin film ceramic PCBs, where precision and miniaturization support advanced diagnostic equipment and implantable devices.
Consumer electronics benefit from the miniaturization capabilities of thin film ceramic PCBs, making them suitable for smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices. Telecommunications infrastructure, including base stations and signal processors, also uses these PCBs for efficient operation in high-performance systems.
In high-power electronics, thin film ceramic PCBs are used for power amplifiers and power supplies, where effective thermal management and reliability are essential. Their unique properties make them a valuable choice for a wide range of high-performance and miniaturized electronic applications.
FAQs
What are Thin Film Ceramic PCBs?
Thin Film Ceramic PCBs are circuit boards with a thin ceramic substrate and conductive films deposited to form circuit patterns. They are known for high precision, improved electrical performance, and compactness.
What types of Thin Film Ceramic PCBs are available?
Types include single-layer, multi-layer, hybrid, and custom thin film ceramic PCBs, each designed to meet different performance and design needs.
What is the fabrication process for Thin Film Ceramic PCBs?
The process includes material preparation, thin film deposition, patterning, etching, surface finishing, assembly, and testing.
What are the typical applications of Thin Film Ceramic PCBs?
Applications include RF and microwave systems, aerospace and defense, medical devices, consumer electronics, telecommunications, and high-power electronics.
Are there any limitations to using Thin Film Ceramic PCBs?
While they offer many benefits, thin film ceramic PCBs can be more expensive than traditional PCBs and require specialized equipment and expertise for fabrication.