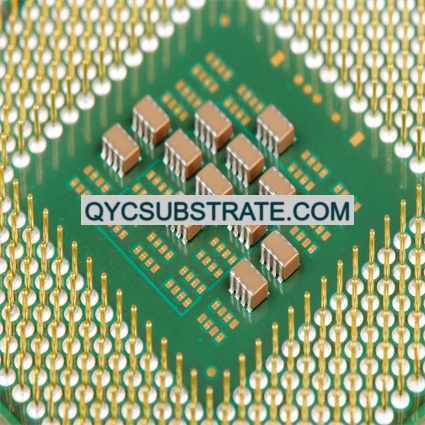
Ultra-Small Size PCB Manufacturer.We specialize in ultra-small size PCB manufacturing, delivering high-precision, compact circuit boards tailored for advanced electronic applications. Our cutting-edge technology ensures reliability and performance in the smallest form factors, meeting stringent industry standards and customer requirements for miniaturized electronic devices.
What is an Ultra-Small Size PCB?
An ultra-small size PCB, or ultra-miniature printed circuit board, is engineered to be exceptionally compact while still supporting intricate electronic circuits. These PCBs are specifically designed to fit into very tight spaces, making them essential for applications where every millimeter counts. The challenge with ultra-small PCBs is packing a high density of components and connections into a tiny footprint while maintaining functionality and performance.
The Types of Ultra-Small Size PCBs
Ultra-small size PCBs can be classified into various types based on their configurations and intended applications. Single-layer ultra-small PCBs are the simplest, featuring just one layer of conductive material and an insulating substrate. These are used in basic applications where complexity is minimal.
For more advanced needs, multi-layer ultra-small PCBs come into play. These boards have several layers of conductive and insulating materials, stacked to allow for more complex circuits and higher density. The multiple layers enable intricate designs while still adhering to compact size constraints.
Flexible PCBs, which are made from bendable materials, offer additional versatility for ultra-small designs. Their flexibility allows them to conform to irregular shapes or fit into non-flat spaces, making them ideal for devices that need to adapt to different forms.
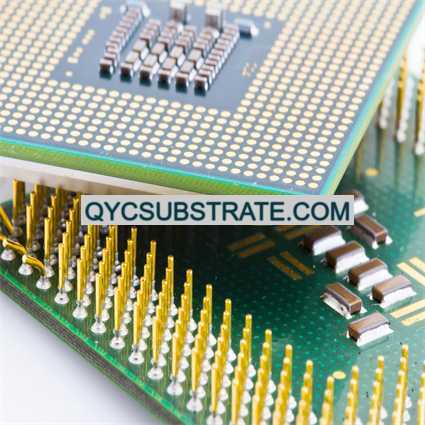

Ultra-Small Size PCB Manufacturer
Rigid-flex PCBs combine the rigidity of traditional PCBs with the flexibility of flexible PCBs. This hybrid design provides both durability and adaptability, catering to applications that require a mix of rigidity and flexibility within a constrained space.
Custom ultra-small PCBs are designed to meet specific needs that may not be covered by standard types. These custom boards might incorporate unique features or materials tailored to particular performance criteria, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in miniature electronics.
The Advantages of Ultra-Small Size PCBs
Ultra-small size PCBs offer several key advantages, particularly in applications where space is a critical factor. The primary benefit is their ability to maximize space efficiency, allowing electronic devices to become smaller and more compact. This is crucial in modern technology, where miniaturization is often a necessity.
Reducing the size of the PCB also results in a decrease in the overall weight of the device. This weight reduction is important for portable and wearable technology, where user comfort and ease of use are paramount.
Despite their small size, these PCBs can support a high degree of design flexibility. Engineers can integrate complex circuits and multiple functionalities within a small area, enabling the creation of advanced and compact devices.
Miniaturization can also lead to enhanced performance. The shorter signal paths and reduced size of the PCB can result in improved signal integrity and faster signal transmission, which is beneficial for high-speed and high-frequency applications.
The compact nature of ultra-small PCBs fosters innovation, allowing for the development of new types of devices and technologies that were previously unfeasible or impractical due to size constraints.
How to Design an Ultra-Small Size PCB
Designing an ultra-small size PCB involves several crucial steps to ensure that the board meets all necessary performance and manufacturing requirements. The process begins with defining the specific needs of the application, including electrical, thermal, and mechanical constraints. This initial step is essential for determining the design specifications and selecting appropriate components.
The next phase involves choosing miniature components that fit within the size limitations of the PCB. These components might include small-outline integrated circuits (SOICs), chip resistors, and micro connectors, all of which are crucial for maintaining functionality in a compact form factor.
A detailed circuit schematic is then created, outlining all components and their connections. This schematic serves as the basis for the PCB layout, which is developed using advanced PCB design software. The layout process includes placing components and routing traces in a way that optimizes space usage while ensuring functionality.
Defining the layer stack-up is another critical aspect, especially for multi-layer PCBs. This involves specifying the arrangement and thickness of each layer to meet electrical and thermal requirements while adhering to size constraints.
Design rules and constraints are established to ensure that the layout adheres to manufacturing capabilities and avoids issues during operation. These rules cover aspects such as trace widths, spacing, and component placement.
Simulation and analysis are performed to verify the design’s performance, including checks for signal integrity and thermal behavior. This step is crucial for identifying and addressing potential issues before the board is fabricated.
Once the design is finalized, fabrication files are prepared, and the PCB is manufactured. Due to the small size, specialized equipment and techniques may be required to achieve precise manufacturing and assembly.
Why Use Ultra-Small Size PCBs Over Other Boards?
The primary reason for using ultra-small size PCBs is their ability to fit into extremely tight spaces, which is essential for many modern electronic devices. This compactness allows for the creation of smaller and lighter devices, which is critical in fields such as consumer electronics, medical devices, and wearable technology.
The design flexibility offered by ultra-small PCBs enables the integration of complex circuits and functionalities into a small area, which supports the development of advanced technologies. Additionally, the miniaturization of PCBs can lead to improved performance characteristics, such as enhanced signal integrity and faster data transmission.
Ultra-small PCBs also foster innovation by allowing for the creation of new types of compact devices that push the boundaries of what is possible in electronics design.
What is the Ultra-Small Size PCB Fabrication Process?
The fabrication of ultra-small size PCBs involves several specialized steps to ensure high-quality results. It begins with selecting appropriate materials for the PCB substrate and conductive layers, which must meet the specific requirements for electrical performance and size constraints.
The preparation of layers involves applying and patterning the conductive material with high precision to achieve the fine features required for ultra-small designs. This step is followed by drilling and forming vias, which are essential for establishing electrical connections between layers.
The circuit patterns are created using etching techniques, which must be accurate to ensure the small features are properly formed. Component placement is carried out with automated equipment, which handles the tiny dimensions of the components and ensures precise alignment.
Soldering and assembly follow, utilizing techniques suited for small-scale processes. This might include reflow soldering or solder paste printing, tailored to fit the miniature size of the PCB.
Finally, rigorous testing and quality control are performed to ensure that the ultra-small PCB meets all performance and reliability standards. This includes electrical testing, visual inspection, and mechanical measurements.
The Application of Ultra-Small Size PCBs
Ultra-small size PCBs are utilized in a wide range of applications where compactness is essential. In consumer electronics, they enable the creation of smaller and lighter devices such as smartphones, tablets, and wearable technology.
Medical devices benefit from ultra-small PCBs by enabling the development of compact diagnostic equipment, implantable devices, and monitoring systems. Their small size allows integration into devices that require precise and reliable electronic components.
In wearable technology, including smartwatches and fitness trackers, ultra-small PCBs fit into the compact and ergonomically designed enclosures, allowing for advanced functionality in a small form factor.
Automotive electronics also make use of ultra-small PCBs for various components such as sensors and control units. The compact design supports the integration of advanced features in space-constrained environments.
FAQs
What is an ultra-small size PCB?
An ultra-small size PCB is a printed circuit board designed to be highly compact while still supporting complex electronic circuits, essential for applications where space is limited.
What types of ultra-small size PCBs are there?
Types include single-layer, multi-layer, flexible, rigid-flex, and custom designs, each tailored to specific applications and space constraints.
What are the advantages of ultra-small size PCBs?
Advantages include space efficiency, weight reduction, design flexibility, enhanced performance, and fostering innovation in compact electronic designs.
How is an ultra-small size PCB designed?
The design process involves defining requirements, selecting components, creating schematics and layouts, defining layer stack-ups, performing design rule checks, simulating performance, and preparing for fabrication.