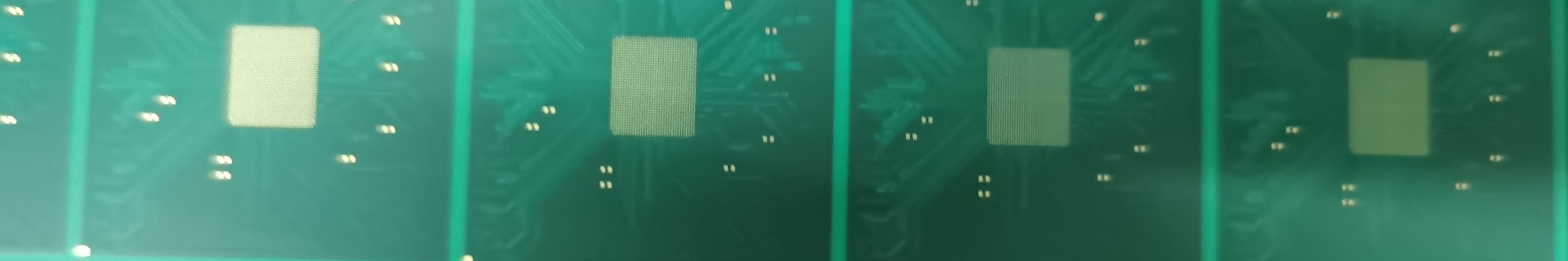
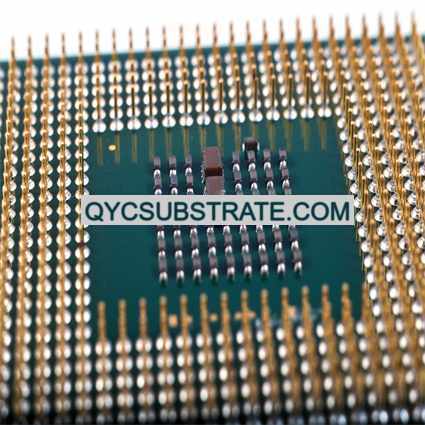
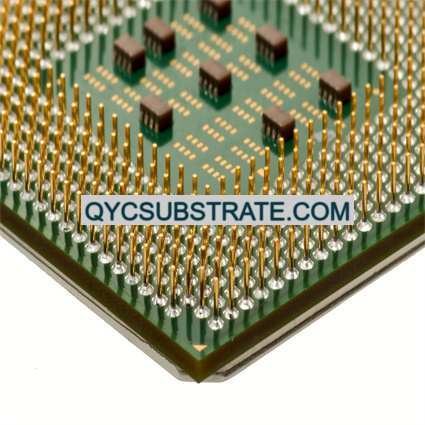
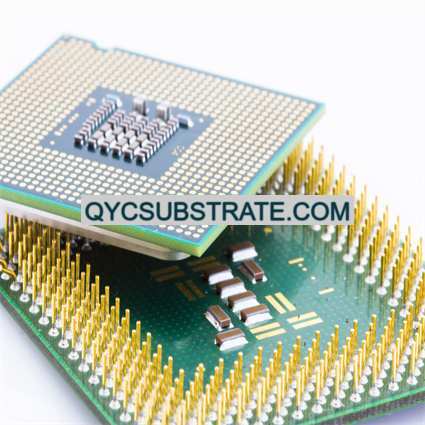
What is Alumina (Al₂O₃) Ceramic PCBs?
Alumina (Al2O3) Ceramic PCBs Manufacturer.We specialize in the production of high-quality alumina (Al2O3) ceramic PCBs. Our PCBs are known for their excellent thermal conductivity, electrical insulation, and mechanical strength. They are ideal for high-performance and high-reliability applications in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics. Our advanced manufacturing processes ensure precision and durability, meeting the highest industry standards.
Alumina (Al₂O₃) ceramic PCBs are advanced circuit boards made from alumina, a material known for its excellent electrical insulation, thermal conductivity, and mechanical strength. Alumina, also known as aluminum oxide, is a versatile ceramic material used in various high-performance electronic applications where traditional PCB materials may fall short.
Alumina ceramic PCBs are crafted from aluminum oxide powder, which is processed and sintered to create a dense, robust substrate. This substrate provides a stable and reliable foundation for mounting electronic components and conducting electrical signals. The high purity of alumina contributes to its superior properties, making it a preferred choice for applications requiring reliable electrical performance and effective heat dissipation.
The Types of Alumina (Al₂O₃) Ceramic PCBs
Alumina (Al₂O₃) ceramic PCBs come in several types, each designed to meet specific application requirements and performance criteria. The primary types include single-layer alumina PCBs, multi-layer alumina PCBs, and custom-designed alumina substrates.

Alumina (Al2O3) Ceramic PCBs Manufacturer
Single-layer Alumina PCBs are the simplest type, consisting of a single layer of alumina material. These PCBs are typically used in applications where straightforward circuit designs are sufficient. Despite their simplicity, single-layer alumina PCBs offer excellent electrical insulation and thermal management properties.
Multi-layer Alumina PCBs feature multiple layers of alumina stacked and bonded together. This multi-layer configuration allows for more complex circuit designs and greater functionality within a compact form factor. Multi-layer alumina PCBs are particularly useful in high-density applications where multiple signal layers and effective thermal management are required.
Custom-designed Alumina Substrates are tailored to meet specific needs of advanced applications. These substrates can include unique features such as integrated heat sinks, specialized patterns for enhanced thermal performance, or embedded components. Custom designs are often used in specialized technologies where standard alumina PCBs may not meet the required specifications.
Each type of alumina ceramic PCB offers distinct advantages based on the complexity and requirements of the application. Single-layer boards are cost-effective and suitable for simpler designs, while multi-layer and custom-designed alumina PCBs provide enhanced functionality and performance for more demanding applications.
The Advantages of Alumina (Al₂O₃) Ceramic PCBs
Alumina (Al₂O₃) ceramic PCBs offer several significant advantages over traditional PCB materials, making them a valuable choice for high-performance and high-reliability applications.
Alumina provides outstanding electrical insulation properties, making Al₂O₃ ceramic PCBs ideal for high-voltage applications. The high dielectric strength and low electrical losses of alumina ensure reliable performance in circuits where maintaining electrical isolation is critical.
Alumina ceramic PCBs have good thermal conductivity, which helps manage heat dissipation in electronic devices. While not as high as materials like Aluminum Nitride (AlN), alumina still provides effective thermal management, which is crucial for preventing overheating and maintaining stable performance in power electronics.
Alumina is known for its hardness and mechanical strength. Al₂O₃ ceramic PCBs offer excellent resistance to physical stress, vibrations, and shocks compared to traditional PCB materials. This mechanical robustness makes alumina PCBs suitable for use in demanding environments where durability is essential.
Alumina ceramics can operate at elevated temperatures without significant degradation in performance. The high temperature tolerance of Al₂O₃ PCBs makes them suitable for applications involving high thermal conditions, such as automotive and industrial electronics.
Alumina has excellent chemical resistance, making Al₂O₃ ceramic PCBs suitable for use in corrosive environments. This property is beneficial for applications in chemical processing, industrial settings, and other scenarios where traditional PCB materials may be susceptible to chemical damage.
Compared to some advanced ceramic materials, alumina is relatively cost-effective. It offers a balance of performance and affordability, making it an attractive option for a wide range of electronic applications.
In summary, the advantages of Alumina (Al₂O₃) ceramic PCBs include excellent electrical insulation, high thermal conductivity, mechanical strength, high temperature tolerance, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness. These benefits make Al₂O₃ ceramic PCBs a valuable choice for various high-performance electronic systems.
How to Design an Alumina (Al₂O₃) Ceramic PCB
Designing an Alumina (Al₂O₃) ceramic PCB involves several key steps to ensure optimal performance and manufacturability. The design process begins with defining the electrical and mechanical requirements of the application, followed by the creation of a detailed circuit schematic and layout.
Start by defining the specific requirements of the application, including electrical specifications, thermal management needs, and mechanical constraints. Understanding these requirements will guide the design choices and material selection.
Choose alumina as the primary substrate material for the PCB. Alumina’s excellent electrical insulation and thermal conductivity properties make it suitable for high-performance applications. Select appropriate conductive materials for the traces and vias that will be used in conjunction with alumina.
Develop a detailed circuit schematic that outlines the components and their connections. This schematic serves as the foundation for the PCB layout and ensures that all necessary electrical functions are included in the design.
Using PCB design software, create a detailed layout of the Al₂O₃ PCB. The layout should include the placement of components, routing of conductive traces, and design of thermal management features. Pay attention to minimizing signal paths, reducing parasitic effects, and ensuring proper spacing to avoid interference.
Incorporate thermal management solutions into the alumina PCB design to address heat dissipation needs. This may include features such as thermal vias or integrated heat sinks to enhance heat transfer away from high-power components.
Ensure that the design adheres to manufacturing capabilities and constraints. This includes considering factors such as layer alignment, via sizes, and component placement to facilitate efficient fabrication and assembly.
Verify the design’s performance through simulations and testing. This includes checking electrical performance, thermal management efficiency, and mechanical durability. Address any issues identified during this phase before proceeding to manufacturing.
Prepare the design files for fabrication, including detailed specifications for the alumina substrate and conductive patterns. Work with a manufacturer experienced in alumina PCB production to ensure high-quality results. The fabrication process will involve sintering the alumina substrate, applying conductive patterns, and assembling the final PCB.
In conclusion, designing an Alumina (Al₂O₃) ceramic PCB involves defining requirements, selecting materials, creating circuit schematics and layouts, integrating thermal management solutions, and ensuring manufacturability. Proper design practices and verification are essential to achieving a high-performance alumina PCB that meets the needs of advanced electronic applications.
Why Use Alumina (Al₂O₃) Ceramic PCBs Over Other Boards?
Alumina (Al₂O₃) ceramic PCBs offer several advantages compared to traditional PCB materials, making them a preferred choice for specific high-performance applications.
Alumina provides excellent electrical insulation, making Al₂O₃ ceramic PCBs ideal for high-voltage and high-frequency applications. The high dielectric strength and low electrical losses of alumina ensure reliable performance in circuits with demanding electrical requirements.
Although not as high as some advanced materials like Aluminum Nitride (AlN), alumina still offers good thermal conductivity. This property helps manage heat dissipation, which is crucial for preventing overheating and maintaining stable performance in power electronics.
Alumina is known for its hardness and mechanical durability. Al₂O₃ ceramic PCBs offer superior resistance to physical stress, vibrations, and shocks compared to traditional PCB materials, making them suitable for harsh environments and demanding applications.
Alumina ceramics can operate at elevated temperatures without significant performance degradation. This high temperature tolerance makes Al₂O₃ PCBs suitable for applications involving extreme thermal conditions, such as automotive and industrial electronics.
Alumina has excellent resistance to chemical corrosion, making Al₂O₃ ceramic PCBs suitable for use in environments exposed to harsh chemicals. This property is beneficial for applications in chemical processing and industrial settings where traditional PCB materials may be vulnerable to chemical damage.
Alumina is relatively cost-effective compared to some advanced ceramic materials. It provides a balance of performance and affordability, making it an attractive option for a wide range of electronic applications.
In summary, Alumina (Al₂O₃) ceramic PCBs offer several advantages over traditional PCB materials, including superior electrical insulation, good thermal conductivity, mechanical strength, high temperature tolerance, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness. These benefits make alumina ceramic PCBs a valuable choice for high-performance and reliability-critical applications.
What is the Alumina (Al₂O₃) PCB Fabrication Process?
The fabrication process of Alumina (Al₂O₃) ceramic PCBs involves several specialized steps to produce a high-performance circuit board that leverages the unique properties of alumina. The process begins with the preparation of alumina substrates and progresses through various stages to achieve the final PCB.
The process starts with the preparation of alumina powder, which is mixed with binders and additives to form a ceramic paste. This paste is then used to create the Al₂O₃ substrate. The mixture is carefully controlled to ensure the desired properties of the final PCB, including electrical insulation, thermal conductivity, and mechanical strength
The alumina paste is shaped into substrates using techniques such as pressing, extrusion, or casting. The substrates are then dried and subjected to a high-temperature sintering process to fuse the alumina particles together and form a solid, rigid material. The sintering temperature typically ranges from 1500°C to 1700°C, depending on the specific alumina formulation.
Once the alumina substrates are prepared, the next step is to pattern the conductive elements onto the substrate. This is typically done using techniques such as screen printing, sputtering, or chemical vapor deposition (CVD) to apply metal layers, such as copper or silver, onto the alumina surface. The conductive patterns form the electrical traces, pads, and vias needed for the PCB.
If the design involves multiple layers, the patterned alumina substrates are laminated together using high-pressure and high-temperature processes. This step ensures that the layers are firmly bonded and aligned to create a multi-layer PCB. Additional components, such as heat sinks or passive elements, may be integrated during this stage.
After lamination, the PCB may undergo surface finishing processes to enhance its performance and appearance. This may include plating with gold or other metals to improve solderability and protect the conductive traces. Surface finishes also help to ensure reliable electrical connections and prevent oxidation.
The final step in the fabrication process involves rigorous testing and inspection to ensure that the alumina PCB meets the required specifications. This includes electrical testing to verify connectivity and performance, dimensional inspection to ensure accuracy, and environmental testing to evaluate the PCB’s performance under various conditions.
In conclusion, the fabrication process of Alumina (Al₂O₃) ceramic PCBs involves material preparation, substrate formation, patterning, lamination, surface finishing, and testing. Each step is carefully controlled to produce high-performance alumina PCBs that leverage the unique properties of alumina for advanced electronic applications.
The Application of Alumina (Al₂O₃) Ceramic PCBs
Alumina (Al₂O₃) ceramic PCBs are used in a wide range of applications due to their excellent electrical insulation, thermal conductivity, and mechanical strength. These properties make alumina PCBs suitable for various high-performance and high-reliability electronic systems.
Alumina ceramic PCBs are commonly used in power electronics applications, such as power converters, inverters, and motor drives. The good thermal conductivity of alumina helps manage heat dissipation in high-power devices, ensuring reliable operation and efficiency. Alumina PCBs are particularly valuable in applications where effective heat management is crucial.
The excellent electrical properties of alumina make it ideal for RF and microwave applications. Alumina ceramic PCBs are used in communication systems, radar equipment, and satellite technology, where high-frequency signal integrity is essential. The low electrical losses and high dielectric strength of alumina ensure reliable performance in these demanding applications.
In the automotive industry, alumina ceramic PCBs are used in various applications, including engine control units (ECUs), power electronics, and advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS). The mechanical strength and temperature tolerance of alumina make it suitable for automotive environments, where reliability and performance are critical.
Alumina ceramic PCBs find use in various industrial applications, including sensors, control systems, and power supplies. The chemical resistance and mechanical durability of alumina make it suitable for harsh industrial environments where traditional PCB materials may not perform adequately.
In the medical field, alumina ceramic PCBs are used in devices requiring high reliability and precision, such as diagnostic equipment and implantable devices. The excellent electrical insulation and thermal conductivity of alumina contribute to the performance and safety of medical electronics.
Alumina PCBs are used in high-temperature electronics applications, such as aerospace and geothermal systems, where traditional PCB materials would fail due to thermal degradation. The high temperature tolerance of alumina ensures that these PCBs maintain their performance and reliability under extreme conditions.
In summary, Alumina (Al₂O₃) ceramic PCBs are utilized in diverse applications, including power electronics, RF and microwave devices, automotive electronics, industrial applications, medical devices, and high-temperature electronics. The unique properties of alumina make these PCBs a valuable choice for high-performance and reliability-critical applications across various industries.
FAQs
What are the main advantages of Alumina (Al₂O₃) ceramic PCBs?
Alumina (Al₂O₃) ceramic PCBs offer excellent electrical insulation, good thermal conductivity, mechanical strength, high temperature tolerance, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness. These advantages make them suitable for high-performance and reliability-critical applications.
How do Alumina (Al₂O₃) ceramic PCBs compare to traditional PCB materials?
Alumina ceramic PCBs provide superior electrical insulation, better thermal conductivity, and greater mechanical strength compared to traditional materials. While they are generally more expensive, their performance benefits make them ideal for high-power, high-voltage, and harsh environment applications.
What are the typical applications of Alumina (Al₂O₃) ceramic PCBs?
Alumina ceramic PCBs are used in power electronics, RF and microwave devices, automotive electronics, industrial applications, medical devices, and high-temperature electronics. Their unique properties make them suitable for a wide range of high-performance applications.
What is the fabrication process for Alumina (Al₂O₃) ceramic PCBs?
The fabrication process includes material preparation, substrate formation, patterning, lamination (if multi-layered), surface finishing, and testing. Each step is carefully controlled to ensure high performance and durability of the final alumina PCB.
Can Alumina (Al₂O₃) ceramic PCBs be used in high-temperature environments?
Yes, alumina ceramic PCBs can operate at elevated temperatures without significant degradation in performance. They are suitable for high-temperature applications, such as aerospace and geothermal systems.
 QYC SUBSTRATE
QYC SUBSTRATE