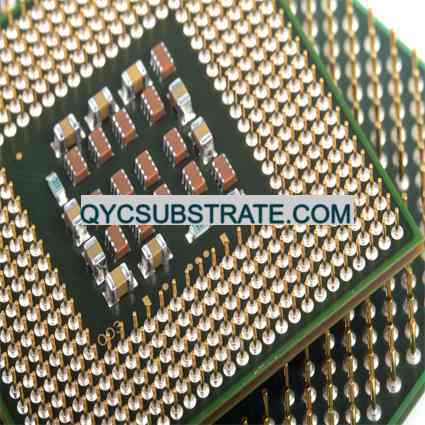
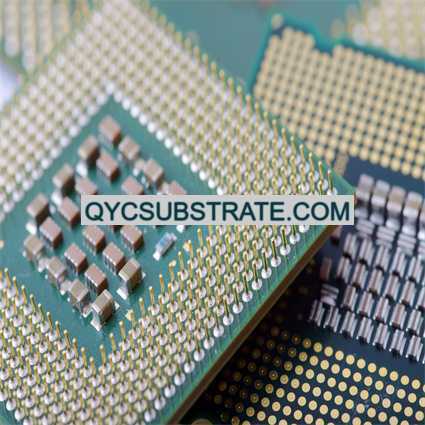
What are Other High Speed Materials PCBs?
Other High Speed Materials PCBs Manufacturer.Our company specializes in the production of high-speed materials PCBs, offering advanced solutions for demanding electronic applications. We utilize state-of-the-art materials and manufacturing techniques to ensure superior performance and reliability. From ultra-low loss materials to advanced thermal management solutions, our 고속 PCBs meet the rigorous requirements of industries such as telecommunications, 항공 우주, and high-frequency electronics. Trust us to provide innovative and reliable PCB solutions tailored to your specific high-speed needs.
Other High Speed Materials PCB (폴리염화비페닐) (Other High Speed Materials PCBs) refer to printed circuit boards used for high-speed and high-frequency circuit applications. These PCBs use advanced materials that are different from traditional FR-4 materials. Traditional FR-4 materials perform well in low-frequency and general applications, but in high-speed signal transmission and high-frequency applications, signal loss and delay increase significantly, so other materials are needed to meet more stringent performance requirements.
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE): PTFE is a material with extremely low dielectric constant and dielectric loss that is particularly suitable for use in high-frequency and microwave circuits. Its excellent electrical performance minimizes signal loss during transmission, ensuring signal integrity.

다른 고속 재료 PCB 제조업체
Polyimide (원주율): Polyimide material has excellent high temperature resistance and mechanical strength, and can work stably in high temperature environments. Its unique electrical properties allow it to perform well in certain high-frequency applications.
Ceramic materials: Ceramic substrates are often used in high-power applications and high-frequency circuits, such as LED lighting and RF power amplifiers, due to their extremely high thermal conductivity and electrical insulation. Ceramic PCB can effectively dissipate heat and improve the overall stability of the circuit.
These high-speed material PCBs can provide significant performance improvements in design and application. 예를 들어, PTFE’s low dielectric constant reduces delay and distortion during signal transmission, while ceramic materials help dissipate heat efficiently in high-power applications.
또한, other high-speed material PCBs are widely used in many high-tech fields, 통신 장비와 같은, automotive electronics, medical equipment, and aerospace. These fields have extremely high performance requirements for circuit boards and need to ensure that the circuit can operate stably under high-frequency and high-speed conditions. 그러므로, choosing a suitable high-speed material PCB is key.
요약하면 다음과 같습니다, other high-speed material PCBs represent a class of circuit boards that can meet the needs of modern high-frequency and high-speed electronic applications. These circuit boards use advanced materials and technologies to provide better electrical performance and reliability.
The types of Other High Speed Materials PCBs
High-speed material PCB (인쇄 회로 기판) is specially designed for high-frequency signal transmission and high-speed data processing, using a variety of high-performance materials to meet different application needs. Here are the main types of high-speed material PCBs:
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) PCB is a high-performance material widely used in high-frequency and microwave circuits due to its extremely low dielectric constant and dielectric loss. PTFE has excellent insulation properties and thermal stability, making it an ideal choice for handling high-frequency signals. Although the cost of PTFE material is higher, its advantages in signal integrity and stability make it particularly important in demanding electronic equipment.
Polyimide (원주율) PCB is another common high-speed material PCB that is favored for its excellent high-temperature resistance. Polyimide materials can maintain good electrical properties and mechanical strength in high-temperature environments and are suitable for use in high-temperature electronic equipment and military electronic products. Although the cost of PI PCB is higher, its high temperature stability and durability make it perform well in harsh environments.
Ceramic PCB uses ceramic substrate, which has excellent thermal conductivity and electrical insulation, and is widely used in high-power and high-frequency equipment. Ceramic materials not only effectively dissipate heat, but also maintain stable electrical performance in high-power applications. Due to their high thermal conductivity and electrical isolation, ceramic PCBs are particularly suitable for use in areas such as LED lighting, high-frequency amplifiers and radar systems.
Improved versions of FR-4 materials can also be used in certain high-frequency applications. Although its electrical performance is not as good as PTFE or PI materials, through the optimization of material formulation, high-frequency FR-4 PCB can provide sufficient performance within a certain frequency range. They are generally lower cost and suitable for applications where performance requirements are not extreme, such as consumer electronics and general communications equipment.
Aluminum-based PCBs, while not typically a “고속” 재료, can provide good performance in certain high-power applications. The aluminum substrate has good heat dissipation capabilities and can support the stable operation of high-power circuits. Commonly used in fields such as LED lighting and power converters.
Each high-speed material PCB has its specific application scenarios and advantages. Choosing the appropriate material depends on the actual technical requirements and economic budget. By understanding the characteristics of these materials, designers can better meet the needs of high-frequency, high-speed circuits.
The advantages of Other High Speed Materials PCBs
High-speed material PCB (인쇄 회로 기판) has many significant advantages over traditional FR-4 materials, making it play a key role in modern electronic equipment. The following are the main advantages of high-speed material PCB:
High-speed material PCB uses materials with low dielectric constant (디케이) 그리고 낮은 유전 손실 (디에프), such as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) and polyimide (원주율), which can effectively reduce signal loss during transmission. This low signal loss characteristic is critical for high-speed data transmission, ensuring signal integrity and stability.
High-speed material PCBs usually have better thermal management capabilities. 예를 들어, ceramic substrates have extremely high thermal conductivity, which can quickly conduct heat away from electronic components, preventing overheating from negatively affecting circuit performance and reliability. Good thermal performance helps improve the stability and life of the overall system.
High-speed material PCB can significantly reduce electromagnetic interference (이엠아이) and crosstalk through special design and material selection. This characteristic is particularly important for the processing of high-frequency signals, which can reduce the impact of noise on signal quality and improve the overall electromagnetic compatibility of the equipment.
High-speed material PCBs are capable of supporting higher frequencies and are suitable for radio frequency (RF) and microwave applications. Materials such as PTFE have extremely low dielectric constants and can effectively transmit signals at high frequencies without causing significant signal attenuation or distortion. This makes high-speed material PCBs particularly important in communications and radar systems.
Many high-speed material PCBs, especially ceramic and polyimide substrates, have excellent chemical stability and high temperature resistance. These materials can operate stably for a long time in harsh environments and are suitable for applications requiring high durability, such as aerospace and automotive electronics.
High-speed material PCBs allow engineers to use higher-density wiring layouts and more complex circuit structures in designs. Lower dielectric constant and loss characteristics enable designs to maintain good electrical performance at higher frequencies, providing greater design flexibility.
전반적, high-speed material PCBs provide strong support for modern electronic devices through their low signal loss, excellent thermal performance, electromagnetic compatibility, frequency support, durability and design flexibility, enabling them to be used in many high-performance applications. Become an indispensable choice in applications.
How to Design a Other High Speed Materials PCBs?
Designing other high-speed material PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards) involves several critical steps that ensure the board performs stably and reliably in high-speed signal transmission. The following are the main steps in the design process:
Before starting the design, you first need to clarify the functional requirements, operating frequency and usage environment of the circuit. This includes determining the circuit’s signal type (such as high-frequency signals, microwave signals, 등.), the size and shape of the circuit board, and the requirements for electromagnetic compatibility (EMC (주)) and thermal management.
Select appropriate high-speed materials based on design needs. 예를 들어, polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is suitable for ultra-high frequency applications and has extremely low dielectric constant and loss; 구체의 (원주율) material is suitable for high-temperature applications and has excellent heat resistance; ceramic PCB is suitable for applications that require High power and good thermal conductivity applications.
Use circuit design software (such as Altium Designer, Cadence, 등.) to draw the circuit schematic diagram. The schematic diagram should accurately reflect the functional requirements of the circuit and the connection relationships between components.
Perform routing in PCB design software, focusing on the design of signal paths. When wiring, try to avoid long traces and sharp corners to reduce signal transmission delays and reflections. Use differential signal pairs and ground plane design to reduce noise and interference.
For high-speed signals, impedance matching is key. Proper trace width and spacing need to be designed to ensure impedance matching. Typically, signal integrity analysis is performed through simulation tools to verify whether the design meets performance requirements.
디자인 프로세스 중, electromagnetic interference (이엠아이) 및 전자기 호환성 (EMC (주)) must be considered. Reduce interference and ensure circuit stability and performance by adding appropriate ground planes, shielding, and filtering designs.
High-speed material PCBs may generate large amounts of heat under high-frequency operation, so designing an effective heat dissipation solution is crucial. Thermal management efficiency can be improved by adding heat sinks, adding heat transfer layers, or optimizing heat dissipation paths.
After the PCB design is completed, electromagnetic simulation software is used to conduct signal integrity and electromagnetic compatibility testing to simulate performance in the actual working environment. These tests can help identify potential problems and make adjustments and optimizations.
Make PCB samples and conduct actual tests to verify whether the design meets the requirements. Testing includes checking electrical performance, thermal performance, and mechanical strength.
Make necessary adjustments and optimizations based on test results to ensure the reliability and stability of the design. 마침내, it is ready for volume production and the production process is ensured to reliably replicate the design.
Through these steps, other high-speed material PCBs can be designed to meet the needs of high-speed signal transmission, ensuring their performance and reliability in practical applications.
Why use ceramic Other High Speed Materials PCBs over other boards?
When choosing PCB (printed circuit board) 자료, ceramic and other high-speed material PCBs are widely used in high-demand fields because of their unique properties. These materials provide better performance than traditional PCB materials when handling high-frequency, high-power applications. The following are the main advantages of ceramic and other high-speed material PCBs over other circuit boards:
Ceramic PCBs have extremely high thermal conductivity and can effectively dissipate heat away from high-power components. For high-power and high-frequency applications, the excellent thermal management properties of ceramics can significantly improve the reliability and service life of circuit boards and avoid failures caused by overheating.
Ceramic materials provide excellent electrical insulation properties, effectively isolating circuits and reducing electrical interference. This characteristic is particularly important for high-frequency signal transmission, which can reduce signal loss and interference and ensure signal integrity and accuracy.
Ceramics and other high-speed materials such as PTFE and polyimide perform well when handling high-frequency signals. The low dielectric constant and low dielectric loss of ceramics make them particularly suitable for use in radio frequency (RF) and microwave applications, allowing them to support higher frequencies without compromising signal quality.
Ceramic materials have high resistance to chemical corrosion, which allows them to maintain stable performance in harsh environments. For equipment that needs to operate at high temperatures or in corrosive environments, ceramic PCBs provide additional protection.
High-speed material PCB such as ceramics can effectively reduce electromagnetic interference (이엠아이) and improve electromagnetic compatibility (EMC (주)). This advantage is especially important in high-frequency applications, as it can effectively reduce the impact of external interference on the circuit, thereby improving the stability and performance of the overall system.
Ceramics and other high-speed materials generally have a long service life because they can withstand higher temperature changes and long-term electrical stress. They show less performance degradation over time than traditional FR-4 materials, providing greater long-term reliability.
In some advanced applications, such as 5G communications, aerospace and high-end medical equipment, the performance requirements of circuit boards are extremely high. Ceramic and other high-speed material PCBs have become the materials of choice in these fields due to their excellent electrical properties and durability.
요약하면, ceramic and other high-speed material PCBs are particularly outstanding in high-frequency and high-power applications due to their excellent thermal management, electrical insulation, high-frequency performance and chemical stability. Although these materials cost more, their improved performance and reliability make them an indispensable choice in many high-end applications.
What is the Other High Speed Materials PCBs Fabrication Process?
The fabrication process for Other High Speed Materials PCBs, such as those using advanced substrates like PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene), ceramic, or specialized high-frequency FR-4, involves several critical steps to ensure high performance and reliability in demanding applications. Here’s a concise overview of the process:
The process begins with the selection and preparation of high-speed materials. For PTFE PCBs, this involves preparing the PTFE sheets, which are known for their low dielectric constant and loss. For ceramic PCBs, high-purity ceramic substrates are used. The material is cut into the required sizes and cleaned to remove any contaminants that could affect subsequent processes.
Design files are prepared using CAD software. These designs include the layout of the circuit traces, vias, and component placements. The design is then transferred onto a photomask, which is used in the photolithography process. For high-speed materials, precise imaging is crucial due to their unique physical properties.
A photoresist layer is applied to the surface of the substrate. This light-sensitive material will define the circuit patterns. The substrate is then exposed to UV light through the photomask, which causes the photoresist to harden in the areas where light strikes, forming a protective pattern for the subsequent etching process.
In the etching step, the exposed areas of the substrate are chemically etched away to reveal the circuit pattern. For high-speed materials, the etching process must be carefully controlled to avoid damage to the substrate. The choice of etching solution depends on the material used—PTFE, ceramics, or high-frequency FR-4 each requires specific etching solutions.
Vias and holes are drilled into the PCB using precision drills. For high-speed materials, this step must be executed with high accuracy to ensure proper alignment and connectivity. After drilling, the vias and holes are plated with copper to create electrical connections between different layers of the PCB.
For multi-layer PCBs, the next step is lamination. Layers of the circuit board are stacked and bonded together using a high-pressure and high-temperature process. This step is critical for high-speed materials to ensure the layers are uniformly bonded, which affects the overall electrical performance and durability of the PCB.
Once lamination is complete, the PCB undergoes a final etching process to remove any excess copper and define the final circuit pattern. After etching, the board is tested for electrical continuity and performance. High-speed materials require thorough testing to ensure that signal integrity and performance standards are met.
The final step involves applying a surface finish, such as HASL (뜨거운 공기 솔더 레벨링), ENIG (Electroless Nickel/Immersion Gold), or another suitable finish to protect the exposed copper and provide solderability. The PCBs are then cleaned, inspected, and packaged for shipment.
전반적, the fabrication of Other High Speed Materials PCBs is a complex process that requires precise control of each step to achieve the desired performance and reliability. The choice of materials and fabrication techniques is crucial to meeting the stringent requirements of high-speed and high-frequency applications.
The application of ceramic Other High Speed Materials PCBs
High-speed ceramic material PCB is widely used in many high-tech fields due to its superior electrical performance and thermal management capabilities. Here are some of the main application areas:
In high-speed communication equipment, such as base stations, routers and optical fiber communication systems, ceramic material PCB is very suitable for processing high-frequency signals due to its low dielectric constant and high dielectric loss factor. Ceramic materials can effectively reduce signal attenuation and interference, and improve the stability and reliability of data transmission. 예를 들어, in 5G base stations, ceramic PCBs can ensure efficient transmission and processing of high-frequency signals.
The aerospace industry has extremely high performance requirements for electronic components, especially in high-temperature and high-pressure environments. Ceramic PCBs are ideal for use in satellites, radar systems and other aerospace equipment due to their excellent high temperature resistance and thermal conductivity. 이러한 응용 분야에서, ceramic materials can effectively dissipate heat to avoid overheating of electronic components and ensure long-term stable operation of the equipment.
In medical equipment, such as ultrasound scanners, CT scanners, and high-frequency medical instruments, the high electrical insulation and low signal loss characteristics of ceramic PCBs are crucial. These devices need to handle high-frequency signals and need to maintain a high degree of electrical isolation during operation to ensure accurate diagnostic results and device safety. Ceramic PCBs can meet these requirements and improve the overall performance of medical equipment.
Ceramic PCBs are often used in high-power electronic devices such as LED lighting and RF power amplifiers due to their excellent thermal conductivity and electrical properties. 이러한 응용 분야에서, ceramic materials can effectively manage heat and prevent components from overheating, thereby increasing the power output and service life of the device.
In addition to the above main fields, ceramic PCBs also play an important role in the fields of automotive electronics, military electronics, and high-precision instruments. 예를 들어, in battery management systems for electric vehicles, ceramic PCBs can provide efficient thermal management and electrical isolation to ensure system reliability and safety.
전반적, high-speed ceramic material PCB plays a key role in various high-tech applications due to its excellent performance, helping to improve the performance and reliability of equipment.
자주 묻는 질문(FAQ)
What is high-speed material PCB?
High-speed material PCB (printed circuit board) is specially designed for high-frequency and high-speed signal transmission, using special materials such as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), 구체의 (원주율) and ceramics. These materials have excellent electrical properties and thermal stability, allowing PCBs to perform well in high-frequency applications, reducing signal loss and delay.
Why choose high-speed material PCB instead of traditional FR-4?
Traditional FR-4 materials may cause higher signal loss and transmission delay in high-frequency applications, while high-speed material PCBs such as PTFE and ceramics can provide lower dielectric constants and better signal integrity. 또한, these materials have excellent thermal management properties, making them suitable for high-power applications and extreme environments.
What is the cost of high-speed material PCB?
High-speed material PCBs typically cost more than traditional FR-4 PCBs. This is because the high-speed materials themselves are more expensive and the manufacturing process is complex. Although the initial investment is relatively large, its superior performance in high-frequency applications can bring long-term benefits and stability, and it is often the first choice for high-performance and high-reliability applications.
How to choose the appropriate high-speed material PCB?
Several factors need to be considered when choosing a suitable high-speed material PCB: first, the operating frequency and signal rate, second, environmental conditions such as temperature and humidity, and third, thermal needs and electrical performance requirements. Different materials such as PTFE are suitable for very high frequency applications, while ceramics perform better where high heat dissipation capabilities are required.
Is the manufacturing process of high-speed material PCB complicated?
Yes, the manufacturing process of high-speed material PCB is more complicated than traditional PCB. It usually includes steps such as material preparation, pattern printing, 에칭, drilling and copper plating. Each step requires precise control to ensure the performance and reliability of the final product. Especially in high-speed applications, higher precision requirements in design and manufacturing are required.
 QYC 기판
QYC 기판