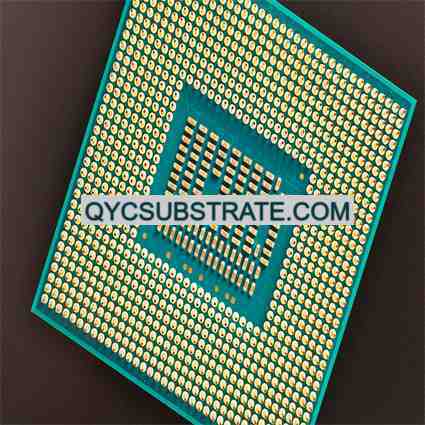
Single-Layer Ceramic PCBs Manufacturer.A Single-Layer Ceramic PCB manufacturer specializes in producing high-performance, heat-resistant circuit boards for advanced electronic applications. These PCBs are designed for superior thermal management, reliability, and compactness, making them ideal for use in industries like aerospace, automotive, and telecommunications. With cutting-edge technology and stringent quality control, the manufacturer ensures precise customization and consistent quality, catering to various customer needs globally..
What is a Single-Layer Ceramic PCB?
Single-layer ceramic PCBs are a type of printed circuit board that features a single layer of ceramic material as the substrate. This substrate is typically made from advanced ceramics such as alumina (Al₂O₃), aluminum nitride (AlNの), or silicon carbide (SiC(シリコン)). These materials are chosen for their excellent thermal conductivity, mechanical strength, and electrical insulation properties, making them ideal for high-performance electronic applications.
The single-layer design means that the circuit patterns are etched or printed on just one side of the ceramic substrate. This simplicity in design is beneficial for applications that do not require complex circuitry but demand high reliability and performance. Single-layer ceramic PCBs are often used in high-temperature environments, high-frequency applications, and situations where efficient heat dissipation is critical.
These PCBs are particularly valued in industries such as power electronics, automotive, 航宇, and telecommunications. The ceramic substrate’s ability to handle extreme temperatures and provide stable performance under challenging conditions sets single-layer ceramic プリント基板 apart from other types of circuit boards.
The Types of Single-Layer Ceramic PCBs
Single-layer ceramic PCBs come in various forms depending on the specific application requirements and the type of ceramic material used. The most common types include those made from alumina (Al₂O₃), aluminum nitride (AlNの), and silicon carbide (SiC(シリコン)). Each material offers distinct advantages, making them suitable for different applications.
単層セラミックPCBメーカー
Alumina-based single-layer ceramic PCBs are widely used due to their excellent electrical insulation and good thermal conductivity. They are commonly found in general-purpose electronic devices and applications where cost-effectiveness is a priority.
Aluminum nitride-based single-layer ceramic PCBs are preferred in applications that require superior thermal management, such as high-power LED lighting and RF modules. The high thermal conductivity of AlN helps dissipate heat efficiently, protecting sensitive electronic components from thermal damage.
Silicon carbide-based single-layer ceramic PCBs are used in extreme environments where both high thermal conductivity and high-temperature stability are required. These PCBs are often found in power electronics and automotive applications, where they can operate reliably under harsh conditions.
Additionally, single-layer ceramic PCBs can be categorized based on the method used to apply the conductive circuit patterns. Thick film and thin film technologies are commonly employed, each offering different levels of precision and performance. Thick film technology is suitable for applications where robust, high-current circuits are needed, while thin film technology is ideal for high-frequency and high-precision applications.
The Advantages of Single-Layer Ceramic PCBs
Single-layer ceramic PCBs offer several significant advantages over traditional PCB materials, particularly in high-performance and demanding applications. One of the primary benefits is their exceptional thermal management capabilities. The ceramic substrate, whether alumina, aluminum nitride, or silicon carbide, provides excellent thermal conductivity, ensuring efficient heat dissipation and preventing overheating of electronic components.
The high mechanical strength and stability of ceramic materials make single-layer ceramic PCBs highly durable and resistant to mechanical stress. This durability is crucial in applications where the PCB is subjected to harsh environmental conditions, such as in automotive, 航宇, and industrial electronics.
Electrical insulation is another key advantage. The ceramic substrate provides excellent electrical insulation, which helps prevent short circuits and enhances the overall reliability of the electronic device. This property is particularly important in high-voltage applications where safety and reliability are paramount.
Single-layer ceramic PCBs also offer superior performance in high-frequency and high-power applications. The low dielectric constant of ceramic materials helps reduce signal loss and maintain signal integrity, making these PCBs ideal for RF and microwave applications. Furthermore, the ability to handle high currents without degradation makes them suitable for power electronics and LED lighting.
The simplicity of the single-layer design is beneficial in applications that do not require complex multilayer circuitry but still demand high performance. This straightforward design can also lead to cost savings in manufacturing, particularly when compared to more complex multilayer or hybrid PCBs.
How to Design a Single-Layer Ceramic PCB
Designing a single-layer ceramic PCB requires a thorough understanding of the application requirements and the properties of the ceramic material being used. The process begins with defining the electrical, thermal, and mechanical specifications of the PCB, including factors such as operating temperature, current load, and frequency.
Once the specifications are defined, the appropriate ceramic material is selected. Alumina is often chosen for general-purpose applications, while aluminum nitride and silicon carbide are selected for applications requiring superior thermal management or high-temperature stability.
The next step involves creating the circuit schematic, which outlines the components and their connections. This schematic is then translated into a PCB layout using design software, where the placement of components and the routing of conductive traces are carefully planned to optimize performance and minimize interference.
For single-layer ceramic PCBs, the circuit patterns are typically created using either thick film or thin film technology. Thick film involves screen printing a conductive paste onto the ceramic substrate and then firing it at high temperatures to form the circuit traces. Thin film, on the other hand, involves depositing a thin layer of metal onto the substrate and then using photolithography to define the circuit patterns.
After the circuit patterns are formed, additional surface finishing processes may be applied, such as metal plating to improve solderability or protective coatings to enhance durability. Finally, the PCB is assembled with the necessary components and subjected to rigorous testing to ensure it meets the required specifications.
Why Use Single-Layer Ceramic PCBs Over Other Boards?
Single-layer ceramic PCBs offer distinct advantages over other types of PCBs, especially in applications where high performance, durability, and thermal management are critical. The use of a ceramic substrate provides superior thermal conductivity, allowing these PCBs to effectively dissipate heat and maintain stable operation even under high-power conditions.
The excellent electrical insulation properties of ceramic materials also contribute to the reliability and safety of single-layer ceramic PCBs. This is particularly important in high-voltage applications, where preventing electrical shorts is essential.
Compared to other types of PCBs, single-layer ceramic PCBs are more resistant to mechanical stress and environmental factors such as temperature fluctuations, humidity, and corrosive substances. This durability makes them suitable for use in harsh environments, including automotive, 航宇, and industrial settings.
Furthermore, the simplicity of the single-layer design can lead to cost savings in manufacturing, as it avoids the complexity and potential issues associated with multilayer or hybrid PCB designs. This makes single-layer ceramic PCBs an attractive option for applications that do not require the additional functionality of multiple layers but still need high reliability and performance.
What is the Single-Layer Ceramic PCB Fabrication Process?
The fabrication process of single-layer ceramic PCBs involves several key steps, beginning with the preparation of the ceramic substrate. The substrate, typically made from alumina, aluminum nitride, or silicon carbide, is carefully processed to achieve the desired thickness and surface finish.
Once the substrate is prepared, the circuit patterns are created using either thick film or thin film technology. In thick film fabrication, a conductive paste is screen-printed onto the ceramic substrate in the desired circuit pattern. The substrate is then fired in a kiln at high temperatures, causing the paste to sinter and form a solid conductive trace.
In thin film fabrication, a thin layer of metal is deposited onto the ceramic substrate using techniques such as sputtering or evaporation. Photolithography is then used to define the circuit patterns, followed by an etching process to remove the excess metal, leaving behind the desired conductive traces.
After the circuit patterns are formed, the PCB may undergo additional surface finishing processes, such as metal plating or the application of protective coatings. These processes enhance the PCB’s performance, solderability, and durability.
The final steps in the fabrication process involve assembling the PCB with the required electronic components and conducting thorough testing to ensure the PCB meets the specified electrical, thermal, and mechanical requirements.
The Application of Single-Layer Ceramic PCBs
Single-layer ceramic PCBs are widely used in various high-performance applications across multiple industries. In power electronics, they are commonly used in power modules, inverters, and LED drivers, where their ability to handle high currents and dissipate heat effectively is crucial.
In the automotive industry, single-layer ceramic PCBs are used in engine control units, powertrain electronics, and lighting systems. Their durability and reliability make them well-suited for the harsh operating conditions found in automotive environments.
Aerospace and defense applications also benefit from the use of single-layer ceramic PCBs. These PCBs are found in avionics, radar systems, and other mission-critical electronic systems, where their high-temperature stability and resistance to mechanical stress are essential.
In telecommunications, single-layer ceramic PCBs are used in RF and microwave systems, 基地局, and signal processors. The low dielectric constant of ceramic materials helps maintain signal integrity, making these PCBs ideal for high-frequency applications.
Medical devices, particularly those requiring high precision and reliability, also utilize single-layer ceramic PCBs. These PCBs are found in diagnostic equipment, sensors, and implantable devices, where their biocompatibility and performance in high-stress environments are advantageous.
よくあるご質問(FAQ)
What are Single-Layer Ceramic PCBs?
Single-layer ceramic PCBs are printed circuit boards with a single layer of ceramic material as the substrate, used in high-performance applications due to their thermal management and electrical insulation properties.
What types of Single-Layer Ceramic PCBs are available?
The types include PCBs made from alumina (Al₂O₃), aluminum nitride (AlNの), and silicon carbide (SiC(シリコン)), each offering different advantages depending on the application requirements.
What are the advantages of Single-Layer Ceramic PCBs?
Advantages include superior thermal management, high mechanical strength, excellent electrical insulation, and reliability in high-frequency and high-power applications.
How is a Single-Layer Ceramic PCB designed?
Design involves defining specifications, selecting the ceramic material, creating circuit schematics, patterning conductive elements, and ensuring the PCB meets performance requirements through rigorous testing.
 QYC基板
QYC基板