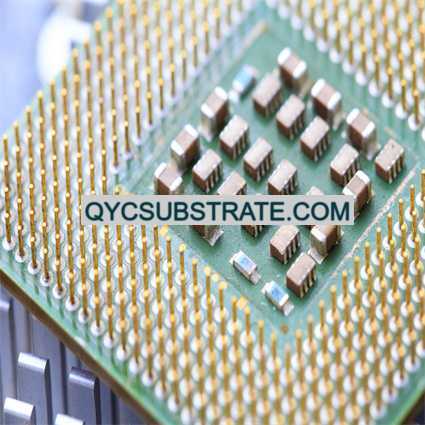
What are High Frequency PCBs?
Others High Frequency PCBs Manufacturer.A high-frequency PCB manufacturer specializes in producing printed circuit boards designed for applications requiring high-speed signal transmission and minimal signal loss. These manufacturers employ advanced materials and technologies to create PCBs that operate effectively at elevated frequencies, ensuring signal integrity and performance. Their expertise encompasses various types of high-frequency PCBs, including those used in telecommunications, radar systems, and high-speed digital devices, making them essential for cutting-edge electronic applications.

Andere Hersteller von Hochfrequenz-Leiterplatten
High Frequency PCBs (HF Leiterplatten) are specialized printed circuit boards designed to handle high-frequency signals, typically in the range of 500 MHz to several GHz. These PCBs are essential in applications where signal integrity and minimal signal loss are crucial, such as in telecommunications, Luft- und Raumfahrt, militärisch, and high-speed computing.
High-frequency signals can be significantly affected by the dielectric properties of the PLATINE Material, Layout des Signalpfads, and environmental factors. Therefore, HF PCBs are made from materials with low dielectric constants (Dk) and low loss tangents (Df) to ensure minimal signal attenuation and distortion. Common materials used for HF PCBs include PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene), Rogers materials, and specialized high-frequency laminates.
The Types of High Frequency PCBs
High Frequency PCBs come in various types and configurations to meet the diverse needs of different applications. Some of the most common types include:
Single-Layer HF PCBs: These PCBs have a single conductive layer and are suitable for simple high-frequency circuits such as antennas and low-noise amplifiers. They offer easy fabrication and lower cost but limited functionality.
Multilayer HF PCBs: These PCBs consist of multiple layers of conductive materials separated by insulating layers. Multilayer HF PCBs are used in more complex applications where multiple high-frequency circuits need to be integrated into a compact space. They offer higher functionality and improved performance but are more complex to manufacture.
Hybrid HF PCBs: Hybrid HF PCBs combine high-frequency materials with traditional PCB materials to achieve specific performance characteristics. Dieser Ansatz ermöglicht es Entwicklern, verschiedene Abschnitte der Leiterplatte für Hochfrequenzleistung und Kosteneffizienz zu optimieren.
Flex and Rigid-Flex HF PCBs: These PCBs offer flexibility in design and are used in applications where the PCB needs to be bent or folded. They are commonly used in aerospace, medizinprodukte, und tragbare Elektronik.
The Advantages of High Frequency PCBs
High Frequency PCBs provide several advantages that make them indispensable in advanced electronic applications:
Superior Signal Integrity: HF PCBs maintain signal integrity by minimizing signal loss and distortion. This is crucial for high-speed data transmission and reliable performance in communication systems.
Low Dielectric Loss: The materials used in HF PCBs have low loss tangents, which reduce signal attenuation and ensure high-frequency signals can travel longer distances without degradation.
Hohe thermische Stabilität: HF PCBs exhibit excellent thermal stability, allowing them to maintain performance and dimensional stability under high-temperature conditions, which is essential for high-power applications.
Mechanical Strength: These PCBs offer robust mechanical properties, enabling them to withstand the physical stresses encountered during assembly and operation.
Compatibility with Advanced Manufacturing Processes: HF PCBs are designed to be compatible with modern manufacturing processes, including automated assembly and high-precision fabrication techniques.
How to Design a High Frequency PCB?
Designing a High Frequency PCB requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure optimal performance. Here are the key steps in the design process:
Choose the appropriate high-frequency material based on the application requirements. Consider factors such as dielectric constant, loss tangent, thermal properties, and mechanical strength.
Maintain precise control over the impedance of transmission lines to ensure signal integrity. Verwenden Sie elektromagnetische Simulationssoftware, um die Impedanz der PCB-Leiterbahnen zu modellieren und zu verifizieren.
Minimieren Sie die Länge hochfrequenter Signalwege, um Signalverluste und Interferenzen zu reduzieren. Use differential pair routing for high-speed differential signals to minimize crosstalk and electromagnetic interference.
Entwerfen Sie robuste Erdungs- und Stromverteilungsnetze, um einen stabilen Betrieb zu gewährleisten und das Rauschen zu minimieren. Use ground planes to provide a low-impedance path for return currents.
Integrieren Sie effektive Wärmemanagementstrategien, wie z. B. Thermal Vias und Kühlkörper, zur Ableitung der von Hochleistungskomponenten erzeugten Wärme und zur Aufrechterhaltung eines stabilen Betriebs.
Stellen Sie sicher, dass das PCB-Design mit den Standard-Fertigungsprozessen kompatibel ist. Arbeiten Sie eng mit dem Leiterplattenhersteller zusammen, um Designparameter und Fertigungsmöglichkeiten zu bestätigen.
Why Use High Frequency PCBs Over Other Boards?
High Frequency PCBs offer distinct advantages over traditional PCBs in specific applications:
HF PCBs are designed to handle high-frequency signals with minimal loss and distortion, making them ideal for high-speed data transmission and communication systems.
The materials and construction techniques used in HF PCBs ensure high reliability and durability, even in harsh operating conditions.
HF PCBs can be customized to meet the specific performance requirements of advanced applications, such as aerospace, militärisch, and high-speed computing.
High Frequency PCBs can be designed in various configurations, inklusive Single-Layer, mehrlagig, hybrid, and flex designs, to accommodate different application needs and form factors.
Mit dem technologischen Fortschritt und der steigenden Nachfrage nach höheren Datenraten und Frequenzen, HF PCBs provide a future-proof solution that can support emerging technologies and standards.
What is the High Frequency PCB Fabrication Process?
The fabrication process of High Frequency PCBs involves several critical steps to ensure high performance and reliability:
Select and prepare the high-frequency laminate material according to design specifications. Das Material sollte auf die erforderlichen Abmessungen zugeschnitten und gereinigt werden, um Verunreinigungen zu entfernen.
Für Multilayer-Leiterplatten, Laminieren Sie die einzelnen Schichten unter hoher Temperatur und hohem Druck miteinander. Stellen Sie sicher, dass die Schichten richtig ausgerichtet und verbunden sind.
Bohrungen von Löchern für Durchkontaktierungen und Bauteilanschlüsse entsprechend dem Designlayout. Präzisionsbohrungen sind unerlässlich, um die Integrität hochfrequenter Signale zu erhalten.
Plattieren Sie die Bohrlöcher und Durchkontaktierungen mit Kupfer, um elektrische Verbindungen zwischen den Schichten herzustellen. Dieser Schritt gewährleistet eine zuverlässige Signalübertragung und mechanische Stabilität.
Übertragen Sie das Schaltungsmuster mittels Fotolithografie auf das Laminatmaterial. Bei diesem Verfahren wird das Material mit einer lichtempfindlichen Folie beschichtet, Er wird durch eine Maske UV-Licht ausgesetzt, und Entwicklung des Musters.
Ätzen Sie das unerwünschte Kupfer weg, um das gewünschte Schaltungsmuster freizulegen. Dieser Schritt erfordert eine präzise Kontrolle, um genaue und saubere Spuren zu gewährleisten.
Auftragen einer Oberflächenveredelung, wie z.B. ENIG (Chemisches Nickel-Immersionsgold) oder HASL (Nivellierung von Heißluftlötmitteln), zum Schutz der Kupferleiterbahnen und zur Gewährleistung einer guten Lötbarkeit.
Führen Sie elektrische Tests und Sichtprüfungen durch, um die Leistung und Qualität der Leiterplatte zu überprüfen. Dazu gehört auch die Überprüfung der Impedanzkontrolle, Signalintegrität, und allgemeine Funktionalität.
The Application of High Frequency PCBs
High Frequency PCBs are used in a wide range of advanced applications due to their superior performance and reliability:
HF PCBs are essential in wireless communication systems, einschließlich Mobiltelefone, Basisstationen, und Satellitenkommunikation. Sie ermöglichen eine Hochgeschwindigkeits-Datenübertragung und eine effiziente Signalverarbeitung.
HF PCBs are used in radar systems, Satellitennavigation, und Kommunikationsgeräte in der Luft- und Raumfahrtindustrie. Ihre hervorragende thermische Stabilität und Zuverlässigkeit gewährleisten eine optimale Leistung in extremen Umgebungen.
HF PCBs are employed in military communication systems, Radar, und Ausrüstung für die elektronische Kriegsführung. Durch ihre robuste Bauweise und hohe Leistung eignen sie sich für geschäftskritische Anwendungen.
HF PCBs are used in advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), Radarsensoren, und Highspeed-Datenkommunikation in modernen Fahrzeugen. Sie gewährleisten einen zuverlässigen Betrieb in rauen Automobilumgebungen.
HF PCBs are used in servers, Rechenzentren, and high-performance computing systems. They enable fast data transfer and processing, supporting the demands of modern computing applications.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
What are the main advantages of High Frequency PCBs?
The main advantages include superior signal integrity, low dielectric loss, hohe thermische Stabilität, mechanical strength, and compatibility with advanced manufacturing processes.
What application areas are suitable for High Frequency PCBs?
High Frequency PCBs are suitable for telecommunications, Luft- und Raumfahrt, militärisch, automotive, and high-speed computing applications, unter anderem.
What is the difference between High Frequency PCBs and traditional PCBs?
High Frequency PCBs offer better signal performance, geringerer Signalverlust, and improved reliability in high-frequency applications compared to traditional PCBs, which are typically used for lower frequency and less demanding applications.
What factors should be considered when designing a High Frequency PCB?
Zu den zu berücksichtigenden Faktoren gehören die Materialauswahl, Impedanzkontrolle, Layout des Signalpfads, Erdung und Power Plans, Thermomanagement, und Herstellbarkeit.
Is the fabrication process of High Frequency PCBs complex?
Der Herstellungsprozess umfasst mehrere präzise Schritte, inklusive Materialaufbereitung, Schichtung, Bohrung, Beschichtung, Schnittmuster-Transfer, Radierung, und Oberflächenveredelung. Obwohl komplex, Diese Schritte sorgen für qualitativ hochwertige und leistungsstarke Leiterplatten.
 QYC-SUBSTRAT
QYC-SUBSTRAT